What is Absenteeism?
Definition, Causes, and Costs for Business
Understanding Absenteeism
Absenteeism goes beyond occasional sick days or emergencies. It becomes a concern when employees consistently fail to report to work, particularly without notifying their supervisors or providing legitimate justification. While some absenteeism is unavoidable, chronic absenteeism can indicate deeper organizational or personal issues that must be addressed.
Why Absenteeism Happens
Absenteeism can arise from a variety of personal and workplace factors, each requiring a tailored approach to address. Common causes include:
- Burnout: Extreme stress and emotional exhaustion from heavy workloads, lack of support, or unrealistic expectations.
- Harassment: Bullying, discrimination, or sexual harassment can make employees avoid the workplace due to fear of confrontation or lack of trust in HR.
- Childcare and Eldercare: Employees without reliable childcare or eldercare options, particularly single parents or caregivers, may need to take unplanned time off.
- Mental Illness: Conditions like depression, anxiety, or PTSD can contribute to absenteeism, especially when stigma or lack of support prevents employees from seeking help.
- Disengagement: Employees who feel undervalued, unchallenged, or disconnected from the company are more likely to skip work without legitimate reasons.
- Injuries or Illnesses: Short-term illnesses, chronic conditions, or injuries can lead to frequent absences, sometimes requiring extended leave.
By recognizing these causes, businesses can implement strategies to address absenteeism and improve employee well-being.
The Costs of Absenteeism
Absenteeism and poor employee health significantly impact U.S. businesses, leading to substantial financial losses. According to the Integrated Benefits Institute (IBI), in 2018, illness-related lost productivity cost U.S. employers approximately $530 billion annually. This figure encompasses various factors, including wages and benefits during absences, impaired performance due to chronic health conditions, medical and pharmacy expenses, workers' compensation costs, and opportunity costs from missed revenues and overtime.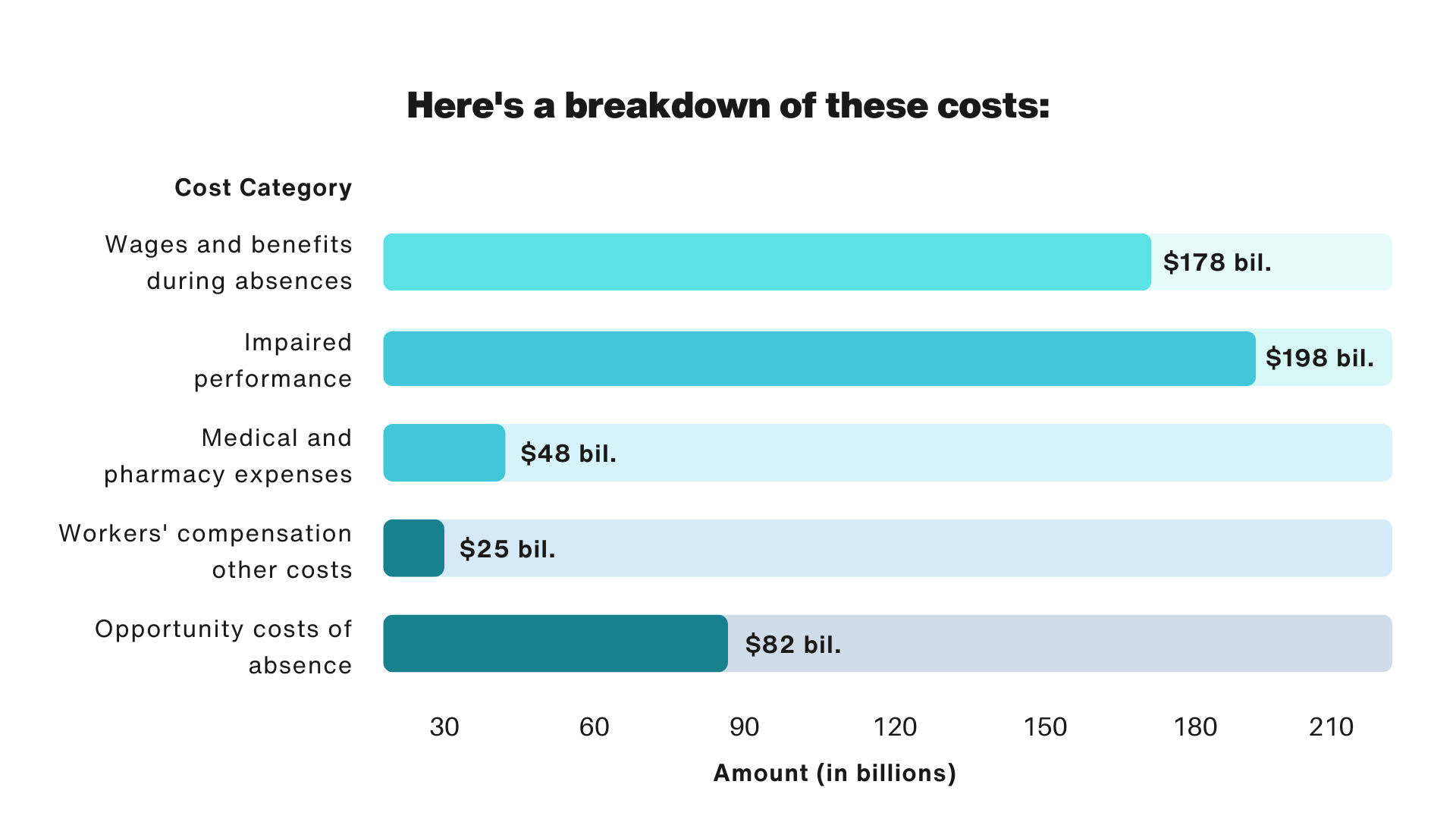
How to Reduce Absenteeism
Reducing absenteeism requires a proactive and strategic approach. Here are some effective methods:
· Promote a positive workplace culture
· Provide mental health support
· Offer flexible work arrangements
· Recognize and reward good attendance
· Conduct regular check-ins with employees
· Improve communication and trust
Example of Absenteeism
Imagine a call center employee who consistently misses work every Monday without explanation. This pattern affects team performance, customer service response times, and the morale of coworkers who must pick up the slack. Over time, the absenteeism becomes a burden on the entire team, highlighting the need for managerial intervention and support.
What is Chronic Absenteeism?
Chronic absenteeism refers to frequent absences that exceed acceptable limits—often defined as missing 10% or more of scheduled workdays. It's a serious issue that can signal deeper problems like disengagement, poor health, or workplace dissatisfaction. Identifying and addressing chronic absenteeism early is crucial.
How Much Absenteeism is Tolerated Before Discipline?
Tolerance levels vary by company and industry, but generally, repeated unexcused absences without documentation or communication may lead to disciplinary action. Employers often implement a progressive discipline policy that starts with verbal warnings, followed by written notices, suspension, and, if necessary, termination.
What Traits Are Connected to More Absenteeism?
Certain employee traits or circumstances are linked to higher absenteeism, such as:
· Low job satisfaction
· Lack of engagement
· High stress levels
· Poor work-life balance
· Inadequate support systems
· Personal or family health issues
Understanding these traits helps employers identify at-risk employees and offer support.
What Traits Are Connected to Less Absenteeism?
Employees who demonstrate high job satisfaction, a strong sense of responsibility, good physical and mental health, effective time management skills, and strong workplace relationships are generally more reliable and consistent in their attendance. By actively fostering these traits through targeted training, wellness initiatives, and employee recognition programs, organizations can significantly reduce absenteeism and promote a more engaged, dependable workforce.
The Impact of Absenteeism on Business
Direct Impacts
Absenteeism affects businesses in several direct ways, leading to immediate disruptions. These include a loss of productivity and revenue as absent employees create gaps in workflow. To compensate, remaining employees may need to work overtime, adding additional costs to the company. Moreover, HR teams bear an administrative burden by managing absences and adjusting schedules, which can also result in reduced overall team performance.
Indirect Impacts
The effects of absenteeism go beyond just operational issues, impacting the broader work environment. Employee morale and engagement can decline as the remaining workforce feels overburdened, leading to frustration and burnout. This often contributes to higher turnover rates, as employees seek more stable environments. Absenteeism also harms customer service due to understaffed teams and can weaken company culture by eroding trust, communication, and collaboration. These factors emphasize the need for proactive absenteeism management.
Prevent Absenteeism in the Workplace
To reduce absenteeism, companies should create supportive environments that address employee needs. This includes offering wellness programs, setting clear attendance policies with incentives, and addressing unscheduled absences promptly. Encouraging healthy employees and open communication helps prevent absenteeism from becoming a recurring issue.
Additionally, companies should investigate the root causes of absenteeism through surveys or one-on-one meetings. Flexible schedules, remote work options, and competitive salaries and benefits also help retain employees and improve attendance. These strategies foster a motivated and engaged workforce, reducing absenteeism in the long run.
Absenteeism is more than just missed days—it’s a critical business issue that can drain resources and harm team dynamics. By understanding the causes of absenteeism and implementing strategic prevention methods, businesses can boost productivity, employee well-being, and organizational success. An engaged, healthy workforce is the key to reducing absenteeism and fostering long-term growth.